Developer Guide for Fitness Duke
Table of Contents
- Developer Guide for Fitness Duke
- Appendix A
- Appendix B
- Appendix C
- Appendix D
- Appendix E
- Instructions for manual testing
- Launch and shutdown of program
- Input of commands
findcommandgeneratecommandquick PLAN_NAME NUMBERcommandippt AGE RUNTIME PUSHUPs SITUPscommandachievementsandclear_achievementscommands and use Casescurrentcommandcancelcommandfinishcommandhistorycommanddatacommanddelete NUMBERcommandsearch KEYWORDcommandplanscommand
- Instructions for manual testing
Acknowledgements
- The CS2113 Team (Professor and Teaching Assistants) For their guidance in teaching us concepts of Software Engineering and OOP
-
AddressBook3 Guidance and examples for OOP and project aspects were used from this repository.
- Exercise Data retrieved from: Wrkout (open source MIT license) Used to generate the data.json file containing all the exercises data used
Design & implementation
Architecture Component
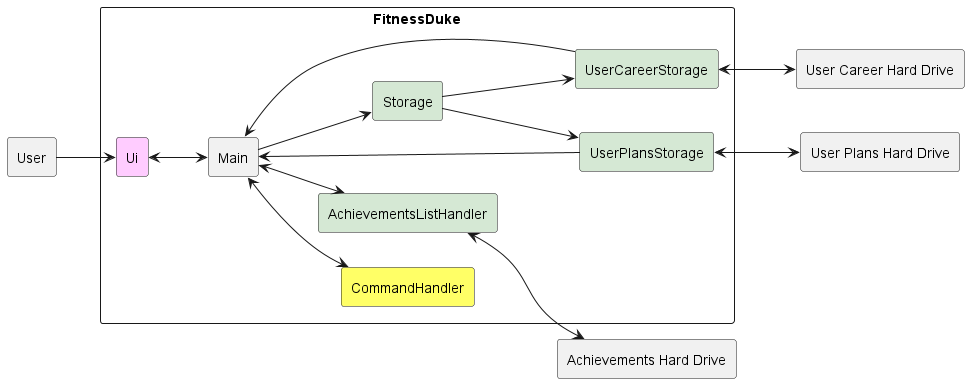
Figure 1.1
The architecture diagram as shown in Figure 1.1 shows us the high level design of Fitness Duke.
The program will first call upon the Storage class. As the storage class extends the UserCareerStorage and UserPlansStorage interfaces, it will point towards both UserCareerStorage and UserPlansStorage. In addition, the program calls upon the AchievementsListHandler class. The respective storages then make use of the User Career Hard Drive, User Plans Hard Drive as well as Achievements Hard Drive to populate its internal memory. When the user then interacts with the program’s UI, the command handler will take over and handle the user’s new commands. New information will then be updated to the respective storages. The storages then update the hard drives accordingly. The process will continue until the user makes no further inputs and exits the program.
Main Components
The architecture comprises five main components.
main: Responsible for the initialisation of user data, app data and connection of various components togetherUi: The User Interface of the appCommandHandler: The main logic controller of the appStorage: Reading and Writing data to and from the hard disk
Hard Drive represents the files in which user data are stored
Interaction of components
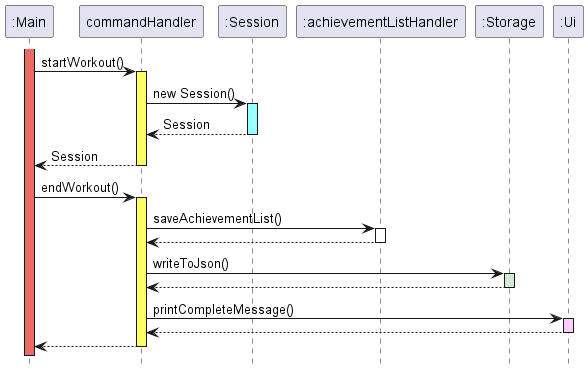
Figure 1.2
The sequence diagram as shown in Figure 1.2 shows the interaction of all the main components when a user enters the
start command and subsequently enters the finish command to simulate the process of a workout session
experienced by the user.
The five main components in the diagram shows the main classes participating in the process.
These classes will be defined into its own API as an interface in the upcoming iteration
More details on these components will be described below.
UI Component
Represented by the Ui class, it handles the interactions between the user and the program. In addition, it also displays a basic overview of what the program does.
Types of pre-defined messages:
- Information messages that describe the functionalities of the program (
Greet,Bye,PrintExercisesclasses) - Help messages that details the usage of the possible commands available in the program (
PrintHelpMessageclass) - Error messages that trigger when a user’s input is incorrect and provides an explanation to the
user. (
ErrorMessagesclass)
The class diagram as shown in Figure 2.1 illustrates the structure of the different classes in Ui.
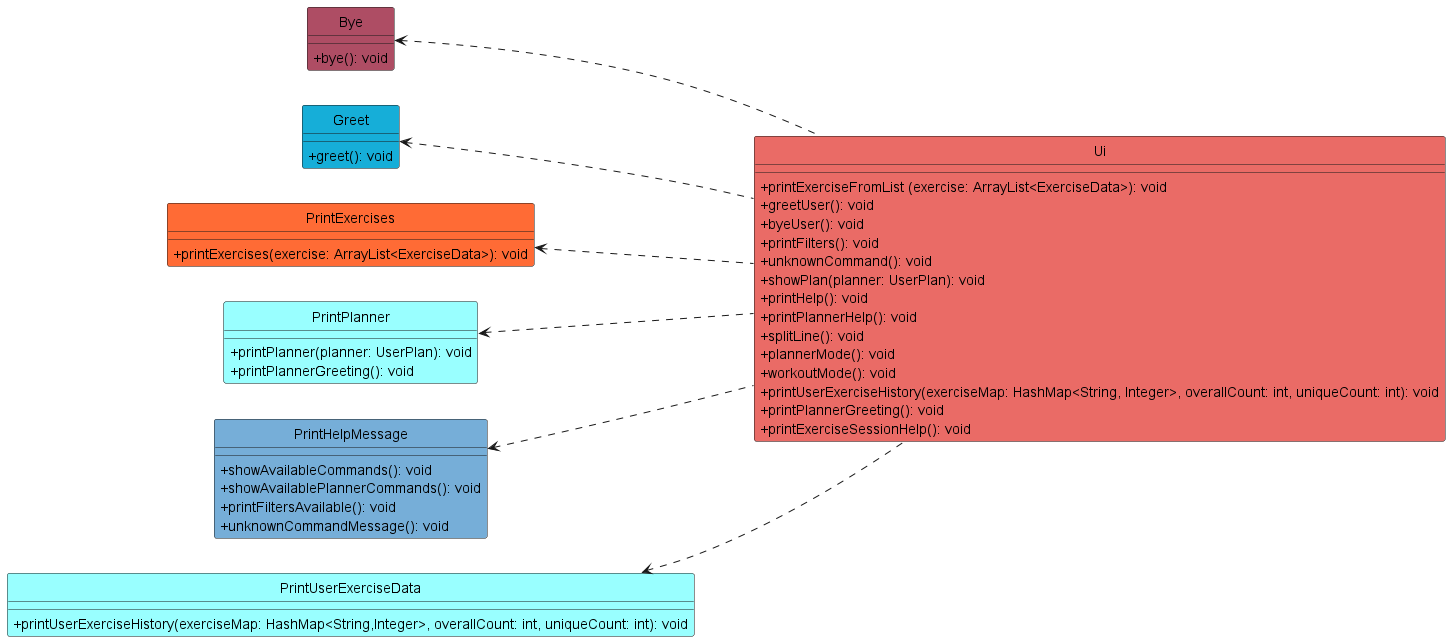
Figure 2.1
Storage Component
API: Storagejava
The Storage component handles the reading and writing of user data to and from the local hard disk in the form of
a json file.
UserCareerData will be stored as userData.json
UserPlan will be stored as plansData.json
Key Aspects:
- Handles the serialization and deserialization of user data into a json file using the Gson Library
- Handles the creation of user data file when previous one is missing or corrupted
- Handles the loading of user data and plans upon start of the program
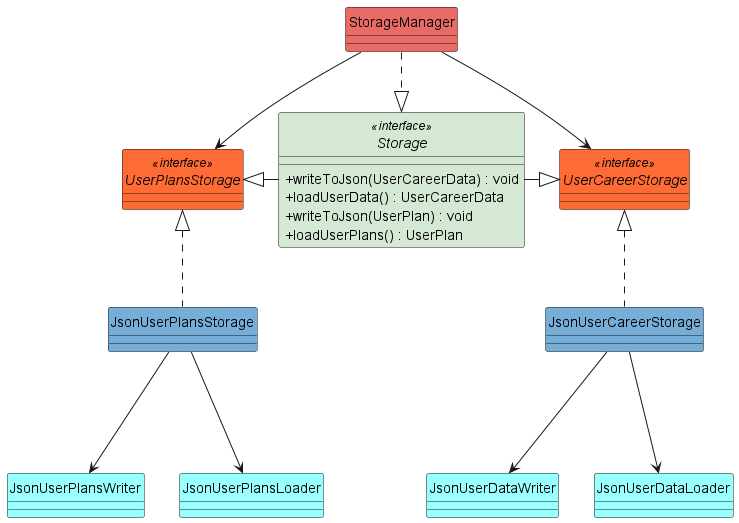
Figure 3.1
The class diagram as shown in Figure 3.1 illustrates the structure of the different classes in Storage.
The Storage Interface is implemented by the StorageManager class.
The StorageManager class is associated with the UserPlansStorage interface which handles the reading and writing of
all UserPlan ,and the UserCareerStorage interface which handles the reading and writing of all
UserCareerData. UserPlansStorage class. These two interfaces are implemented by the JsonUserPlansStorage
and JsonUserCareerStorage classes respectively.
The Storage API interacts with the other classes as shown in the Sequence Diagram as per Figure 3.2 where it shows how the Storage API loads the local user data json file as well as the user plans json file upon the resumption of the program assuming data file is present and not corrupted.
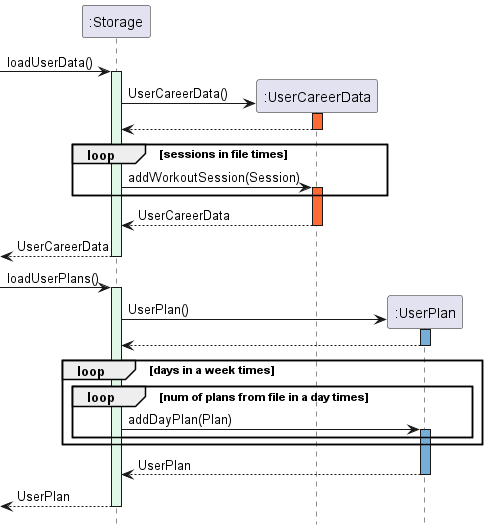
Figure 3.2
During the initialisation of FitnessDuke, the loadUserData method from the Storage API which firstly
instantiates a new UserCareerData object. The method would subsequently iterate and parse through all the
sessions from the local hard disk into the new UserCareerData object.
The populated UserCareerData which now contains all the previous sessions is returned back to be used by the main
method of the program.
This process is similar for the loading of the UserPlan object except where we loop through seven times
(number of days in a week) and for each loop, iterate and parse through each plan from the local hard disk into the
newly instantiated UserPlan object.
In the unlikely event that the user accidentally deleted or modify the json files stored on the hard disk incorrectly, the sequence diagram below as per Figure 3.3 illustrates how the program loads a fresh set of data. This means all previous data will be lost.
There are a few cases where this could happen (non-exhaustive) causing a DukeError to be thrown:
- File missing or not named correctly
- File does not follow json format
- Missing or deleted entries
- Invalid inputs of user data.
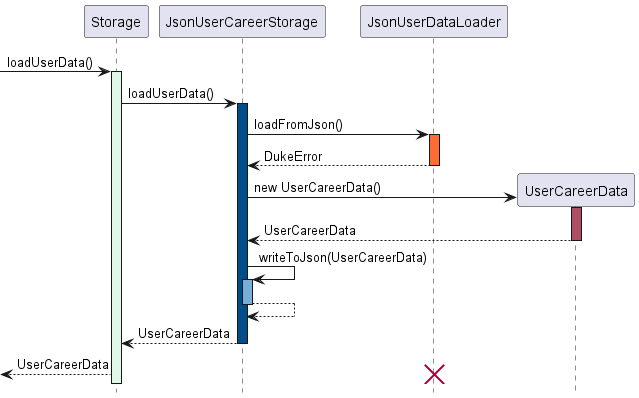
Figure 3.3
As shown in the diagram, a failed attempt in loading user data from the json file would result in the program to
overwrite an existing userData.json file with a blank state.
User data would be written to the json file at various points of the program
The UserCareerData is saved to the json file whenever there is any modifications made to the object during runtime.
This also applies to the UserPlan.
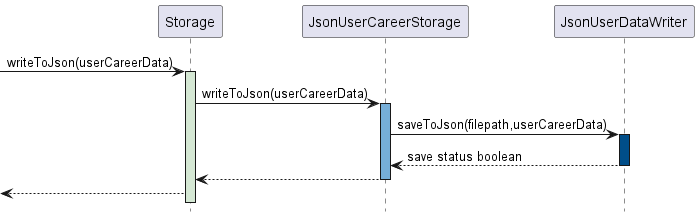
Figure 3.4a
The sequence diagram above as shown by Figure 3.4a illustrates the interaction of Storage components whenever
writeToJson() is invoked for UserCareerData.
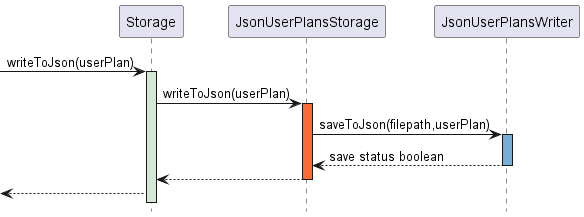
Figure 3.4b
The process for the saving of UserPlan is similar to that of saving UserCareerData as shown in Figure 3.4b. The
figure illustrates the interaction of Storage components whenever writeToJson() is invoked for UserPlan.
Achievement Storage Component
API: AchievementListHandler.java
The storage handler that we have is the achievements list handler, which has seperated logic from the Storagejava
component.
Key Aspects:
- Handles the parsing of achievement data from the text file.
- Handles the creation of user data file when previous one is missing, corrupted or invalid (e.g. When the achievement is completed but for some reason the “requirement” to achieve the data is not met)
- Handles the loading of achievement data at the start of the program and saving achievement data upon the completion of an exercise session.
achievementData will be stored as uachievementData.txt
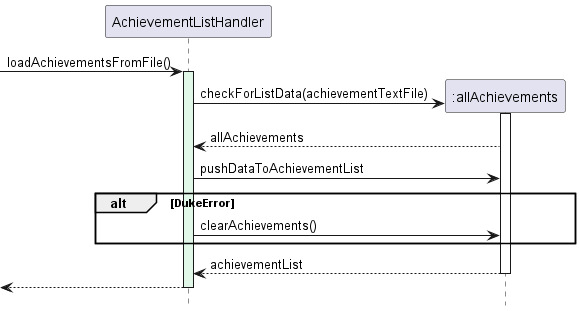
Figure 3.5a
During the initialisation of FitnessDuke, the loadAchievementsFromFile method from the AchievementListHandler
API which searches for the contents of the achievementData File.
Once found, the pushDataToAchievementList is called, parsing all the
text from the local hard disk into the new AchievementListHandler object, which holds the achievementList Data
in an arraylist.
The populated achieventData which now contains all the previous sessions is now stored in the
AchievementListHandler class and can be accessed using the getAchievementList() function from the AchievementListHandler.
More information on this later.
This process is also similar to the loading of the UserPlan, aside from the file being a text file and that there
is more parsing to do due to the object oriented nature of achievements.
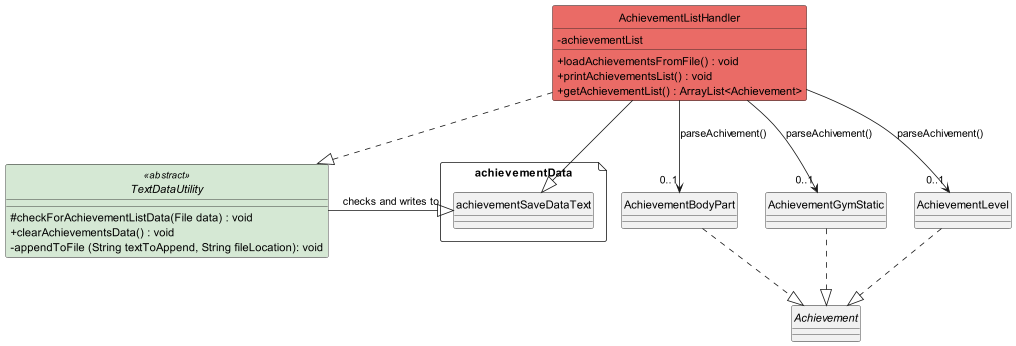
Figure 3.5b
Above shows how there are actually 3 classes (i.e. AchievementBodyPart, AchievementGymStatic, AchievementLevel) that
extend the abstract Achievements class.
The reason why we need to do this is that the way we extract and update data for each achievement is different due to the 3 different categories of filters that we have applied to our generate function. Hence we have 3 different classes.
The AchievementListHandler class uses the parseAchievement() function to parse each line in the text file into their
respective classes and types, creating an achievement for each line. The current pre-loaded list of achievements has
24 achievements, but advanced users can manually add more achievements should they know how to manipulate the data.
(The current 24 filters are attributed to the 8 filters * 3 different diffculties = 24 achievements.)
Command Handler Component
The command handler component consists of multiple states that the program can be at any time. It controls where the user input is being processed.
Key Aspects:
- Handles when there is an exercise ongoing, giving access to finishing and hence saving finished exercises, and keeping track of what exercises there are.
- Handles when there is no exercise ongoing, granting access to generating new exercises with different confines.
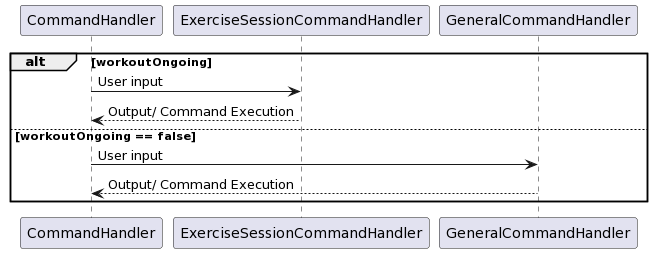
Figure 4.1
ExerciseSessionCommandHandler
The exercise Command Handler is engaged when the user has an ongoing workout. Upon completion of the workout, the user can save their workout if completed, such that the completed workout is logged and will be saved for future reference.
To manage this exists the ExerciseStateHandler, which allows for saving, starting
ending, cancelling workouts.

Figure 5.1
PlannerCommandHandler
The planner Command Handler is engaged when the user enters the workout planner. By implementing a separate Command Handler dedicated for the planning of work-outs, this simplifies the user experience by compartmentalising the secondary planner function, and ensures that users will not be bombarded by a long list of commands in the help menu.
To manage this exists the PlannerCommandHandler, which allows for adding, deleting,
and viewing the workout plans.
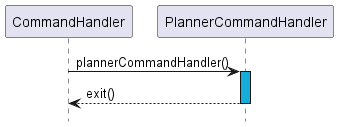
Figure 6.1
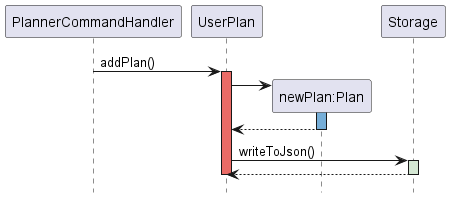
Figure 6.2
Achievements
Achievements are mainly updated upon finishing a workout session.
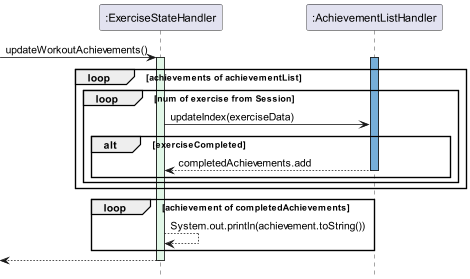
Figure 7.1
When the finish command is called during a workout session, the updateWorkoutAchivements() function is called.
This calls the ExerciseStateHandler class to loop through all the achievements in the achievementList in the
AchievementListHandler class for every single exercise accomplished. This is required as a single exercise can
apply to multiple achievements. For example, an exercise can be both have the “easy” difficulty and “legs” body part
attribute, hence completing that exercise would add to both “legs” and “easy” related exercises.
If an exercise is completed during that specific session, then it is added to an array list in the ExerciseStateHandler
class. Once all the achievements and exercises have been iterated through, the ExercuseStateHandler will print
out all the achieved achievements in the list, congratulating the user.
Exceptions
Accounts for the different scenarios that may trigger an error during user’s interactions with the program
Error Message Handling
Enumeration: [ErrorMessages.java]
All error messages are stored in the ErrorMessage enumeration for easy access across different classes that could
run into similar exceptions.
As the ErrorMessage class is a public enumeration, we are able to compile most of our messages here for error
management purposes as well. This is due to the ability to use the same error message in multiple areas for similar
error cases.
Furthermore the reason why we need so many messages is due to the fact that each error message should be unique to
the error provided.
This can range from a variety of use cases. For example, the achievementListHandler Class might be accessing
corrupt achievement data, hence it calls for the corresponding ERROR+LOAD_CORRUPT_ACHIEVEMENT_DATA error message.
The diagram below shows some, but not all of the use cases of Error Messages.
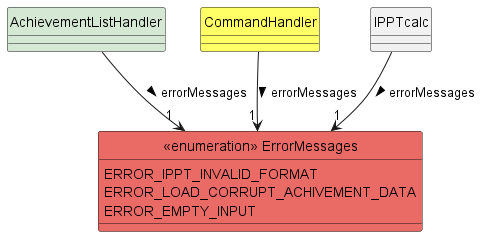
Figure 8.1
Commands
To interact with FitnessDuke, users have to input commands specified with parameters to perform operations which will be passed to the Command Handler to generate a corresponding Command according to their input. There are a total of 3 command handlers for the handling of user inputs, and the CommandList implements each of these command handlers. The general command handler is in use while the user is currently not in a workout session or in the midst of creating a fitness plan.
Upon the starting of a workout session from within the GeneralCommandHandler, the user is then directed to the ExerciseSessionCommandHandler. While within
the handler, the user has access to current, finish and cancel commands.
When the user enters the planner feature, they are redirected to the PlannerCommandHandler. Within the handler,
they then have access to the add PLAN_NAME, delete PLAN_NAME, help as well as exit commands.
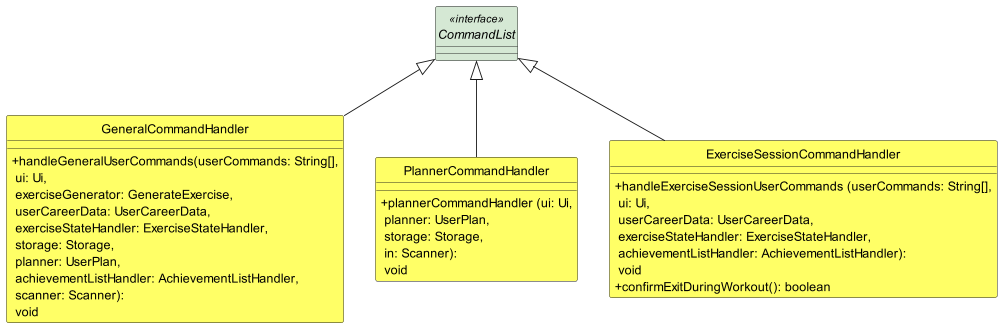
Figure 9.1
Additional features to be added
- A workout planner for the user to add and customise their desired sequence or schedule of workouts.
- An achievement list that will output messages to congratulate the user based on the different milestones of exercises he/she has achieved when using the program.
Appendix A
Product scope
Target user profile
Fitness Duke targets individuals who are looking for a smarter way to keep fit, as well as adding a greater diversity to their workout routines.
Value proposition
With the recent emphasis of healthy lifestyles in Singapore, the Singapore Government has initiated the Healthier SG initiative Healthier SG. To encourage more fitness activities to be carried out by Singaporeans as a form of preventive care, Fitness Duke aims to help Singaporeans to kick-start their journeys towards a healthier lifestyle, regardless of their knowledge in exercises or their individual fitness levels. Through this program, it aims to not only help users learn new workouts, while also keep track of their fitness progress.
Appendix B
User Stories
| Version | As a … | I want to … | So that I can … |
|---|---|---|---|
| v1.0 | - User who wants to start working out - User who wants to train a specific part of my body |
- Select a specific intensity workout - Request a workout that comprises exercises that thoroughly exercises that body part |
- Exercise according to selected intensity - Work on my target body part. |
| V1.0 | - User | - be able to filter my exercises by body part | - train a specific part of my body |
| V2.0 | - User | - be able to start a workout and set it as complete and save it | - reflect and track my progress |
| V2.0 | - User looking for motivation | - be able to track my workout history as statistics | - better visualise my overall progress |
| V2.0 | - user with little to no experience with exercise | - be given instructions for the specific exercise that I am working on | - be educated on how to complete the exercise correctly |
| V2.0 | - User who wants to stay motivated to workout</br>- User who wants to feel good about my past workouts | - See myself be able to accomplish or achieve incrementally greater goals</br>- Keep track of all my exercises | - Continue to stay motivated in making exercise a fun, long-lasting habit |
| V2.1 | - User who likes to be motivated by incentive | - Gain achievements throughout my usage of the app | - Be more motivated to keep exercising |
| V2.1 | - SAF personnel | - Track my IPPT scores over a period of time | - achieve gold ranking in my IPPT |
Appendix C
Non-Functional Requirements
- The program should be able to generate a list of exercises within 5 seconds
- The program should be able to run on any PC (i.e. different OS)
- Be able to handle cases such as user data file corruption - The program is not required to ensure the workouts are carried out safely and properly by the user
- Avoid giving repeated workouts in the same session
Appendix D
Glossary
- FitnessDuke - The name of our application
- OS - Operating Systems - Linux, MacOS, Windows
- CLI - Command Line Interface - The terminal in the PC OS
- ExerciseData - Individual Exercise data from the
data.jsonfile - Ui - User Interface
- UserCareer - The entire usage journey of using our application
Appendix E
Instructions for manual testing
Launch and shutdown of program
- Download the latest version of the jar file and copy the file to the folder where you want the Fitness Duke program to run.
- Run the .jar file based on the instructions on the User Guide. Expected: Shows the CLI with the welcome message. alongside some logging messages.
Input of commands
- Input of unlisted/unknown commands that are not listed in the help command:
Test cases:
o,hi
Expected: Error details will be shown in the terminal
find command
- Find a set of exercises based on a specified keyword :
find KEYWORD - Test case:
findExpected: The list of exercises will not be shown. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case :
find armExpected: The list of exercises containing keywordarmwill be shown.
generate command
- Get a list of workouts
- Test case:
generateExpected: The list of exercises will not be shown. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
generate 2Expected: A list of 2 random exercises will be shown, alongside their respective IDs, names, difficulty levels, workout types and descriptions. - Test case:
generate easyExpected: The list of exercises will not be shown. Error details will be shown in the terminal.
quick PLAN_NAME NUMBER command
- Prerequisites : An existing plan under
plans - Test case:
quickExpected: The list of exercises will not be shown. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
quick home_legs_day 3If planhome_legs_dayis not inplans, error details will be shown in the terminal. Otherwise, list of 3 exercises will be shown related to the workout type.
ippt AGE RUNTIME PUSHUPs SITUPs command
- Takes in user’s inputs of the user’s age and the respective scores for the 3 exercises, and returns the total points the user obtains , as well as adding as a new exercise session.
- Test case:
ipptExpected: The IPPT exercise session will not be added. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
ippt 9 10:00 10 10Expected: The IPPT exercise session will not be added. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
ippt 20 -10:00 10 10Expected: The IPPT exercise session will not be added. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
ippt 20 10:00 -10 10Expected: The IPPT exercise session will not be added. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
ippt 20 10:00 10 -10Expected: The IPPT exercise session will not be added. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
ippt a b c dExpected: The IPPT exercise session will not be added. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
ippt ! @ # $Expected: The IPPT exercise session will not be added. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
ippt 16Expected: The IPPT exercise session will not be added. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
ippt 16 12:00Expected: The IPPT exercise session will not be added. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
ippt 16 12:00 10Expected: The IPPT exercise session will not be added. Error details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
ippt 16 12:00 10 10 10Expected: The IPPT exercise session will not be added. Error details will be shown in the terminal.
achievements and clear_achievements commands and use Cases
For testing purposes, calling the clear_achievements command will clear all the data for a user.
This means that all of the counts of exercises logged by the achievements file is reset to 0, and all completed
achievements are reset to be not achieved.
- Test case:
achievements
Expected: List of the details of all achievements and their corresponding details - Test case:
clear_achievements
Expected: clear_achievement message is shown in the terminal. - Test case:
clear_achievements
achievements
The achievements data should show that there are 0 logged exercises/ 0 exercises done in the achievements list. - Test case:
clear_achievementsgenerate easy 3startfinishachievements
Expected: At least the “Easy Peasy” and the “Easy Peasy Lemon Squeezy” achievements should be printed out in the command line after thefinishcommand. Other achievements might be printed out depending on the exercises generated. The new logged data should show that you have completed 3 easy achievements in the easy related achievements when theachievementscommand is called.
current command
- Displays a list of the user’s current workout exercises.
- Test case :
currentwith no current workout session Expected: There will not be an output of a list of current exercises, details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
currentwith a current workout session Expected: There will be an output of a list of current exercises, details will be shown in the terminal.
cancel command
- Cancels the user’s current workout session, and the workout session is registered as incomplete.
- Test case:
cancelwith no current workout session Expected: There will not be any workout session cancelled, details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
cancelwith a current workout session Expected: The current workout session will be cancelled, details will be shown in the terminal.
finish command
1.Finishes the current workout session, and it is recognised as a complete session.
- Test case:
finishwith no current workout session Expected: There will not be any workout session finished, details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
finishwith a current workout session Expected: The current workout session will be finished, details will be shown in the terminal.
history command
-
Displays the user’s entire career history in using Fitness Duke. It provides details on the sessions completed with the date and time as well as the exercises completed.
- Test case:
historywith no existing completed workout sessions or exercises. Expected: Error message will be output to the user, details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
historywith an existing completed workout session. Expected: Details of the workout session and the completed exercises will show, details will be shown in the terminal.
data command
-
Displays the list of completed exercises, along with the number of times of completion for each exercise. Apart from providing the list of completed exercises, it also outputs the total number of unique as well as non-unique exercises completed at the end of the list.
- Test case:
datawith no existing completed workout sessions or exercises. Expected: Error message will be output to the user, details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
datawith an existing completed workout session. Expected: Details of list of completed exercises along with the total number of exercises completed will show, details will be shown in the terminal.
delete NUMBER command
-
Deletes a completed workout session according to the session number which the user specifies.
- Test case:
delete 1with 2 existing completed workout sessions. Expected: Workout session 1 will be deleted, details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
delete -1with existing completed workout sessions. Expected: Error message will be output to the user, details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
delete 10with only 5 existing completed workout sessions. Expected: message will be output to the user, details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
deletewith existing completed workout sessions. Expected: Error message will be output to the user, details will be shown in the terminal.
search KEYWORD command
- Find exercises from the user’s list of completed exercises which names contain the input keyword. The found exercises contain additional details such as id number, difficulty level, workout type as well as the description of the exercise.
- Test case:
search calfwith existing workout sessions having exercises with keyword ‘calf’ in it. Expected: All exercises within the user’s completed list of exercises containing “calf” will appear. Details will be shown in the terminal. - Test case:
search calfwith existing workout sessions having no exercises with keyword ‘calf’ in it. Expected: Error message will be output stating no matching exercises found.
plans command
1.Displays all workout plans which have been created by the user.
- Test case:
planswith no existing plans created. Expected: Outputs an empty plan in the terminal to the user. - Test case:
planswith existing plans created. Expected: Outputs the existing plans in the terminal to the user.